BaseAdapter Tutorial With Example In Android Studio
Before we share BaseAdapter it is first critical to change
Adapter. In android, a connector is a scaffold between UI part and information
source that causes us to fill information in the UI segment. It holds the
information and send the information to connector see at that point view can
takes the information from the connector view and demonstrates the information
on various perspectives like as rundown see, lattice see, spinner and so forth.
For more customization of perspectives we utilizes the base connector.
Presently lets examine BaseAdapter class.
·
BaseAdapter is a typical base class of a general
usage of an Adapter that can be utilized in ListView, GridView, Spinner and so
forth.
·
At whatever point you require a tweaked rundown
in a ListView or redid lattices in a GridView you make your very own connector
and broaden base connector in that.
·
Base Adapter can be reached out to make a custom
Adapter for showing a custom rundown thing.
Critical Note:
ArrayAdapter is additionally a usage of BaseAdapter.
Here is the code of Custom Adapter when we expands the
BaseAdapter in that:
|
public class CustomAdapter broadens
BaseAdapter {
@Override
public int getCount() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int I) {
return invalid;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int I) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int I, View see,
viewGroup) {
return invalid;
}
|
In the above code piece we see the overrided techniques for
BaseAdapter which are utilized to set the information in a rundown, network or
a spinner. From that point we for the most part utilized two capacities
getCount() and getView().
We should talk about every one of these capacities in
detail:
1. getCount():
The getCount() work restores the aggregate number of things
to be shown in a rundown. It tallies the incentive from exhibit list measure()
strategy or a cluster's length. For instance, in the event that we have a
rundown of components in an arraylist and we need to show the things in a
rundown see then we can check the aggregate number of components utilizing the
size capacity and afterward that whole number esteem is returned by the
capacity getCount() as demonstrated as follows.
|
@Override
public int getCount() {
int count=arrayList.size();/tallies the
aggregate number of components from the arrayList
return tally;//restores the aggregate
tally to connector
}
|
2. getView(int I, View see, viewGroup):
This capacity is naturally considered when the rundown thing
view is prepared to be shown or going to be shown. In this capacity we set the
design for rundown things utilizing LayoutInflater class and afterward add the
information to the perspectives like ImageView, TextView and so forth.
The following is the getView capacity's precedent code with
clarification incorporated into which we set the format utilizing
LayoutInflater and afterward get the view's id and actualize them.
|
@Override
public View getView(int I, View see,
viewGroup) {
view = inflter.inflate(R.layout.activity_gridview,
invalid);//set format for showing things
ImageView symbol = (ImageView)
view.findViewById(R.id.icon);//get id for picture see
icon.setImageResource(flags[i]);//set
picture of the thing's
return view;
}
|
3. getItem(int I):
This capacity is utilized to Get the information thing
related with the predefined position in the informational collection to get the
comparing information of the explicit area in the gathering of information
things.
The following is the precedent code in which we restores the
exhibit rundown's thing as indicated by position.
|
@Override
public Object getItem(int I) {
return arrayList.get(i);
}
|
4. getItemId(int I):
With respect to the getItemId (int position), it restores
the relating to the position thing ID. The capacity restores a long estimation
of thing position to the connector.
The following is the code in which we restores the position.
|
@Override
public long getItemId(int I) {
return I;
}
|
BaseAdapter Example In Android Studio: |
Example 1:
Example of BaseAdapter for showing Animal pictures in matrices utilizing
GridView.
In the underneath example we show creatures pictures as
matrices utilizing custom connector to demonstrate the utilization of
BaseAdapter. The following is the last yield and code with clarification:
Stage 1: Create
another venture and name it BaseAdapterExample.
Stage 2: Now open
res - > design - > activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and include following
code. Here we will make Gridview inside LinearLayout:
|
<?xml version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<GridView
android:id="@+id/simpleGridView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:footerDividersEnabled="false"
android:numColumns="3"/>
</LinearLayout>
|
Stage 3: Create another Activity
activity_gridview.xml inside design and include the beneath code:
|
<?xml version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/symbol"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"/>
</LinearLayout>
|
Stage 3: Now open application - >
java - > package - > MainActivity.java and include the beneath code.
Ensure you have pictures spared in drawable envelope with the names we have
utilized or else change the name dependent on the pictures present in your drawable
organizer.
|
package
example.abhiandriod.baseadapterexample;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.GridView;
public class MainActivity broadens
Activity {
GridView simpleGrid;
int animals[] = {R.drawable.animal13,
R.drawable.animal14, R.drawable.animal15, R.drawable.animal16,
R.drawable.animal17, R.drawable.animal18, R.drawable.animal15,
R.drawable.animal16, R.drawable.animal17};
@Override
ensured void onCreate(Bundle
savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
simpleGrid = (GridView)
findViewById(R.id.simpleGridView);
customAdapter = new
CustomAdapter(getApplicationContext(), creatures);
simpleGrid.setAdapter(customAdapter);
}
}
|
Stage 4: Create another class
CustomAdapter.java inside package and include the accompanying code
|
package
example.abhiandriod.baseadapterexample;/Use your package
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.ImageView;
public class CustomAdapter broadens
BaseAdapter {
Setting;
int animals[];
LayoutInflater inflter;
public CustomAdapter(Context
applicationContext, int[] creatures) {
this.context = applicationContext;
this.animals = creatures;
inflter =
(LayoutInflater.from(applicationContext));
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return animals.length;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int I) {
return invalid;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int I) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int I, view,
viewGroup) {
view =
inflter.inflate(R.layout.activity_gridview, invalid);
ImageView symbol = (ImageView)
view.findViewById(R.id.icon);
icon.setImageResource(animals[i]);
return view;
}
}
|
OutPut :-
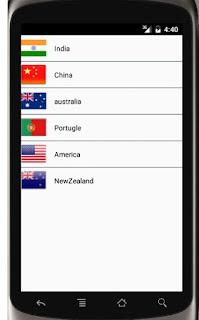
Example 2: Example of BaseAdapter to
show rundown of nations in a ListView utilizing Custom BaseAdapter
In the
beneath example we show rundown of nations with their banners utilizing custom
connector to demonstrate the utilization of BaseAdapter. The following is the
last yield and code with clarification well ordered.
Stage 1: Create another task in Android
Studio and name it BaseAdapterExample
|
Select File - > New - > New
Project. Fill the structures and snap "Complete" catch.
|
Stage 2: Now Open application - >
res - > format - > activity_main.xml (or) main.xml and include following
code :
|
<?xml version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/simpleListView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:divider="@color/material_blue_grey_800"
android:dividerHeight="1dp"
android:footerDividersEnabled="false"/>
</LinearLayout>
|
Stage 3: Now make another XML format.
For our situation, we name it as activity_listview.xml. Include the beneath
code in it. Likewise ensure you have iclauncher picture spared in drawable
envelope or include it.
|
<?xml version="1.0"
encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/symbol"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:padding="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:textColor="#000"/>
</LinearLayout>
|
Stage 4: Now open application - >
java-> package - > MainActivity.java and include the underneath code.
|
package
example.abhiandriod.baseadapterexample;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListView;
public class MainActivity expands
Activity {
ListView simpleList;
String countryList[] =
{"India", "China", "australia",
"Portugle", "America", "NewZealand"};
int flags[] = {R.drawable.india,
R.drawable.china, R.drawable.australia, R.drawable.portugle,
R.drawable.america, R.drawable.new_zealand};
@Override
ensured void onCreate(Bundle
savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
simpleList = (ListView)
findViewById(R.id.simpleListView);
customAdapter = new
CustomAdapter(getApplicationContext(), countryList, banners);
simpleList.setAdapter(customAdapter);
}
}
|
Stage 4: Create new class
CustomAdapter.java and include following code
|
package
example.abhiandriod.baseadapterexample;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class CustomAdapter broadens
BaseAdapter {
Setting;
String countryList[];
int flags[];
LayoutInflater inflter;
public CustomAdapter(Context
applicationContext, String[] countryList, int[] banners) {
this.context = setting;
this.countryList = countryList;
this.flags = banners;
inflter =
(LayoutInflater.from(applicationContext));
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return countryList.length;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int I) {
return invalid;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int I) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int I, view,
viewGroup) {
view =
inflter.inflate(R.layout.activity_listview, invalid);
TextView nation = (TextView)
view.findViewById(R.id.textView);
ImageView symbol = (ImageView)
view.findViewById(R.id.icon);
country.setText(countryList[i]);
icon.setImageResource(flags[i]);
return view;
}
}
|
OutPut :-



No comments:
Post a Comment