Android button Example
Android button Example With Listerner
Android Button speaks to a push-catch. The
android.widget.Button is subclass of TextView class and CompoundButton is the
subclass of Button class.
There are distinctive kinds of catches in android, for
example, RadioButton, ToggleButton, CompoundButton and so on.
Android button Example With Listerner
Here, we will make two textfields and one catch for whole
of two numbers. In the event that client clicks catch, aggregate of two
information esteems is shown on the Toast.
We can perform activity on catch utilizing distinctive
sorts, for example, calling audience on catch or including onClick property of
catch in action's xml record.
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
//code
}
});
<Button
android:onClick="methodName"
/>
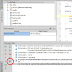
Drag The component of write the code for UI in activity_main.xml
Above all else, drag 2 textfields from the Text Fields
palette and one catch from the Form Widgets palette as appeared in the
accompanying figure.
File :- activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="example.javatpoint.com.sumoftwonumber.MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_conte"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="61dp"
android:ems="10"
android:inputType="number"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="84dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="53dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:ems="10"
android:inputType="number"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="84dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="127dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="109dp"
android:text="ADD"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteX="148dp"
tools:layout_editor_absoluteY="266dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
Activity Class
Now write the code to
display the sum of two numbers.
File: MainActivity.java
package example.javatpoint.com.sumoftwonumber;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText edittext1, edittext2;
private Button buttonSum;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
addListenerOnButton();
}
public void addListenerOnButton() {
edittext1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText1);
edittext2 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.editText2);
buttonSum = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button);
buttonSum.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String value1=edittext1.getText().toString();
String value2=edittext2.getText().toString();
int a=Integer.parseInt(value1);
int b=Integer.parseInt(value2);
int sum=a+b;
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),String.valueOf(sum), Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}
}
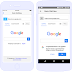
Out Put :-




No comments:
Post a Comment